In the rapidly evolving world of wearable technology, Meta is breaking new ground with its experimental neural wristband. This innovative device has the potential to revolutionize how we interact with computers and virtual environments.
The neural wristband is a wearable device that tracks hand and finger movements by picking up neural electrical signals passing through the nerves in your arm. It uses a non-invasive technique called electromyography (EMG) to capture these signals. Unlike invasive brain implants, this wristband is comfortable to wear, making it accessible and user-friendly.
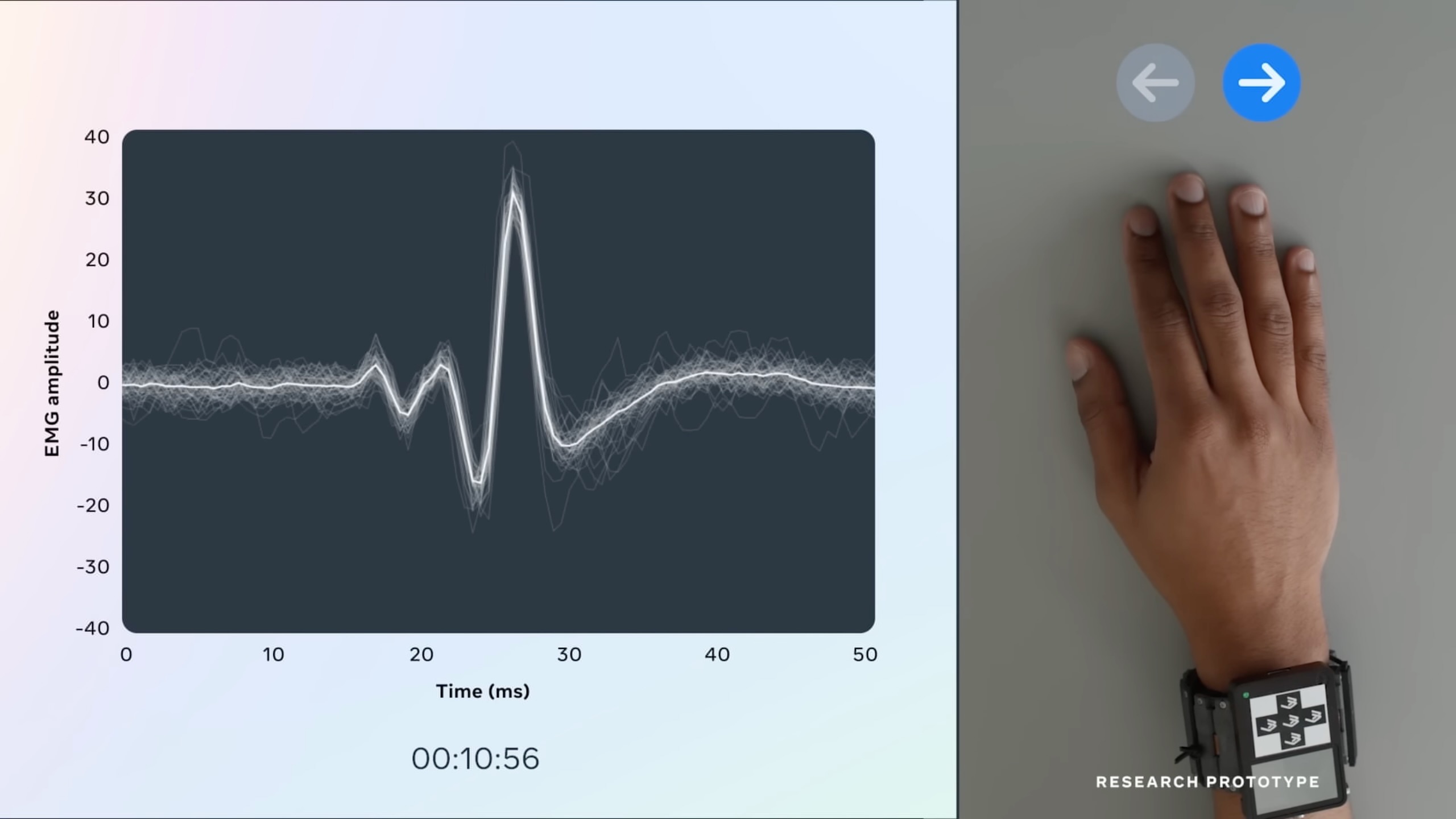
Imagine typing on a keyboard without physically moving your fingers. With Meta’s neural wristband, this futuristic concept is now a reality. By analyzing neural signals, the wristband translates your mental intentions into text input. You can type simply by thinking! No more clunky keyboards or touchscreen taps, just pure cognitive interaction.
Meta’s CEO, Mark Zuckerberg, has been promoting this technology. He envisions a future where users can communicate in real-time through a private and discreet interface. Whether you’re composing an email, chatting with friends, or navigating virtual reality (VR) environments, the neural wristband could be your silent companion.
The neural wristband’s impact extends beyond traditional typing. It has the potential to revolutionize augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) experiences. Imagine wearing AR glasses and composing messages without tapping on a virtual keyboard, simply by thinking. The device’s EMG technology guides electrical signals from your brain to your fingers, enabling precise finger tracking and control.
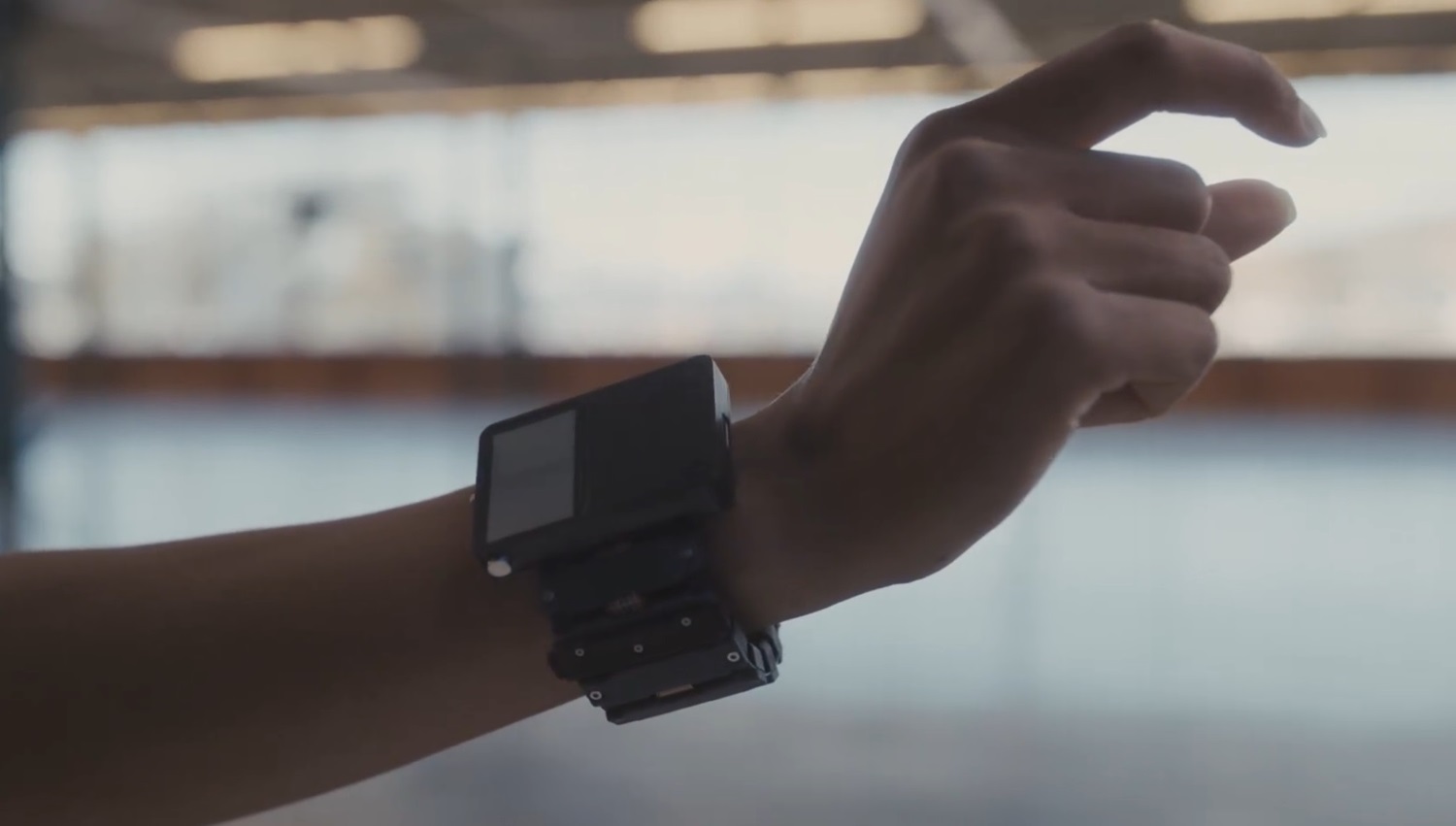

Meta showcased the experimental prototype of this wristband in 2021, and since then, they’ve been refining the technology. In a recent interview, Zuckerberg confirmed that they’re close to launching a market-ready product. He emphasized that this isn’t a one-year project, but rather the culmination of years of research and development.
The neural wristband offers a private and efficient input method. There is no need for brain implants or invasive procedures. Users can communicate seamlessly, whether in a crowded room or a quiet space, without physically moving their hands. It’s a step towards a more intuitive and natural human-computer interaction.
For more such content, keep reading @techinnews



